Fast Registration¶
Fast registration feature, can support millions of instance registration.
This feature is primarily used in scenarios where an ultra-high performance registry is required and is not recommended for scenarios where performance requirements are low or instance levels are small.
This feature is turn off by default, if need fast register you should open the fast registration switch.
When this feature is open, you can call register interface API, the service center will put instances in the queue, then direct return instanceId to users, at last, register registry asynchronously by timing task.
QuickStart Guide¶
1.Config the fast registration queue size, to enable fast registration
If queueSize is bigger than 0, fast registration will trigger
The default configuration of /conf/app.yaml is as follows:
register:
fastRegistration:
# this config is only support in mongo case now
# if fastRegister.queueSize is > 0, enable to fast register instance, else register instance in normal case
# if fastRegister is enabled, instance will be registered asynchronously,
# just put instance in the queue and return instanceID, and then register through the timing task
queueSize: 0
Config queueSize in /conf/app.yaml, for example set queueSize to 50w
register.fastRegistration.queueSize=500000
2.Start service center
./service-center
3.Call the registry interface
Call the registry interface, you will receive InstanceID soon, now a fast registration has been completed once
- Registered instance APIs can be called concurrently
- There is a slight delay between returning the instanceID and actually registering the instance to database, but 100w instance registration delays are within seconds
- If more than 15 minutes did not discovery the instance ,there may be a problem with the environment. The client can register again with the InstanceID that has been generated and return to user
Process Design¶
The flow chart is as follows:
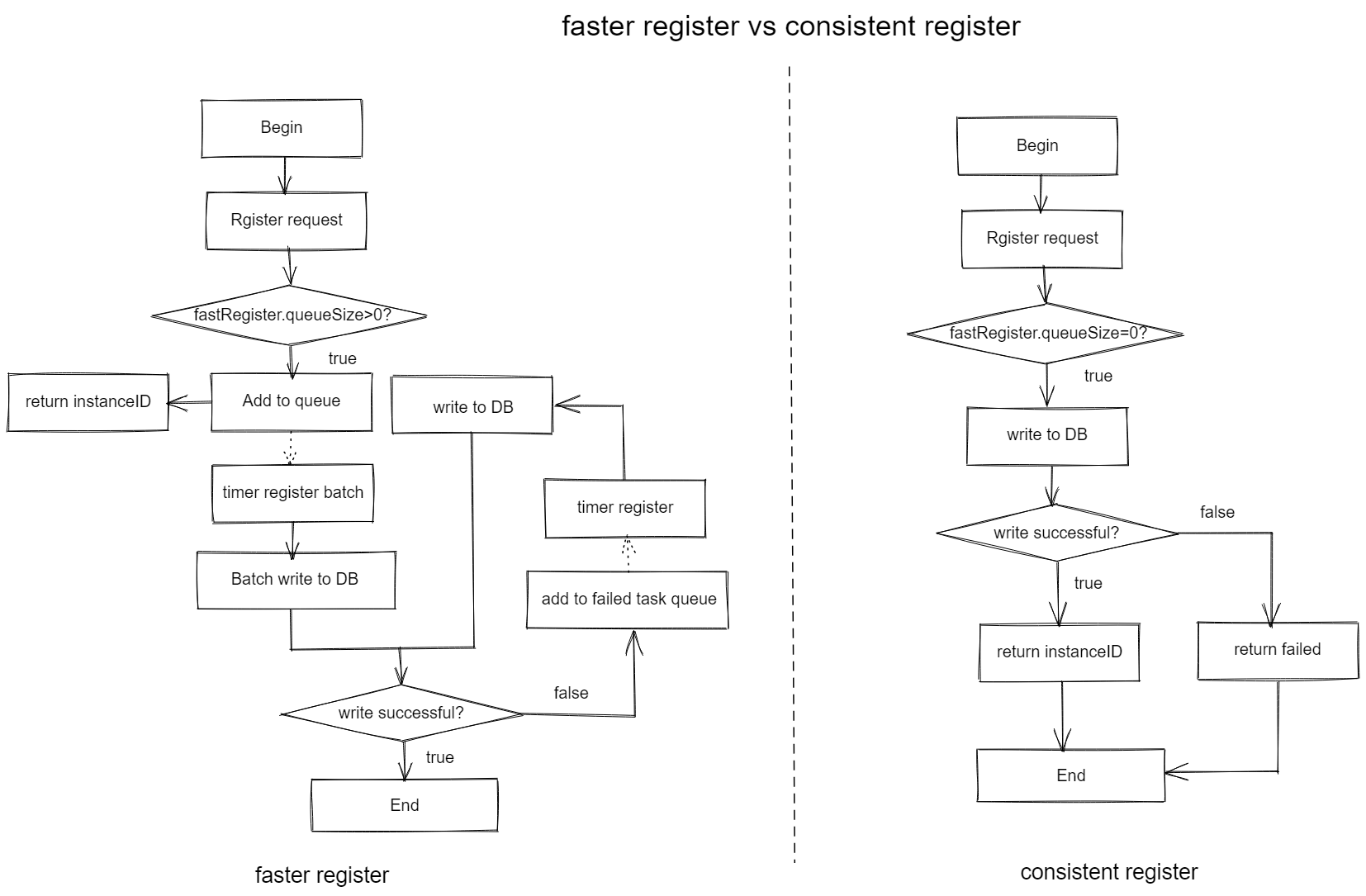 register_image
register_image
Normal Case:
If the fast registration is enabled, it is put in the queue and eventually registered to MongoDB in batch by timed tasks(The time interval is 100 millimeters)
Abnormal Case:
- If the connection between Mongo and service center is broken, and the registration fails, the instance will be put into the failure queue and registered again
- If the registration fails for 3 consecutive times, the fuse will be cut off for 5s and resume after successful registration
- If a single instance fails to register for more than 500 times, the instance will be discarded, and the SDK will register again when the heartbeat finds that the instance does not exist
Attention¶
1.The database with ETCD scenario does not have this feature; only the Mongo database scenario does
2.Because the registration is asynchronous, there will be a certain amount of delay in the registration, the delay is basically in the second level
Performance Test¶
The performance of a fast registration instance is about three times better than that of a normal registration
best performance test:
|service center| mongoDB | concurrency|tps |latency|queueSize| |—-| —-| —-|—-|—-|—-| |8u16g2|16u32g|200|9w |1mm|100w| |16u32g2|16u32g|500|15w|2mm|100w|